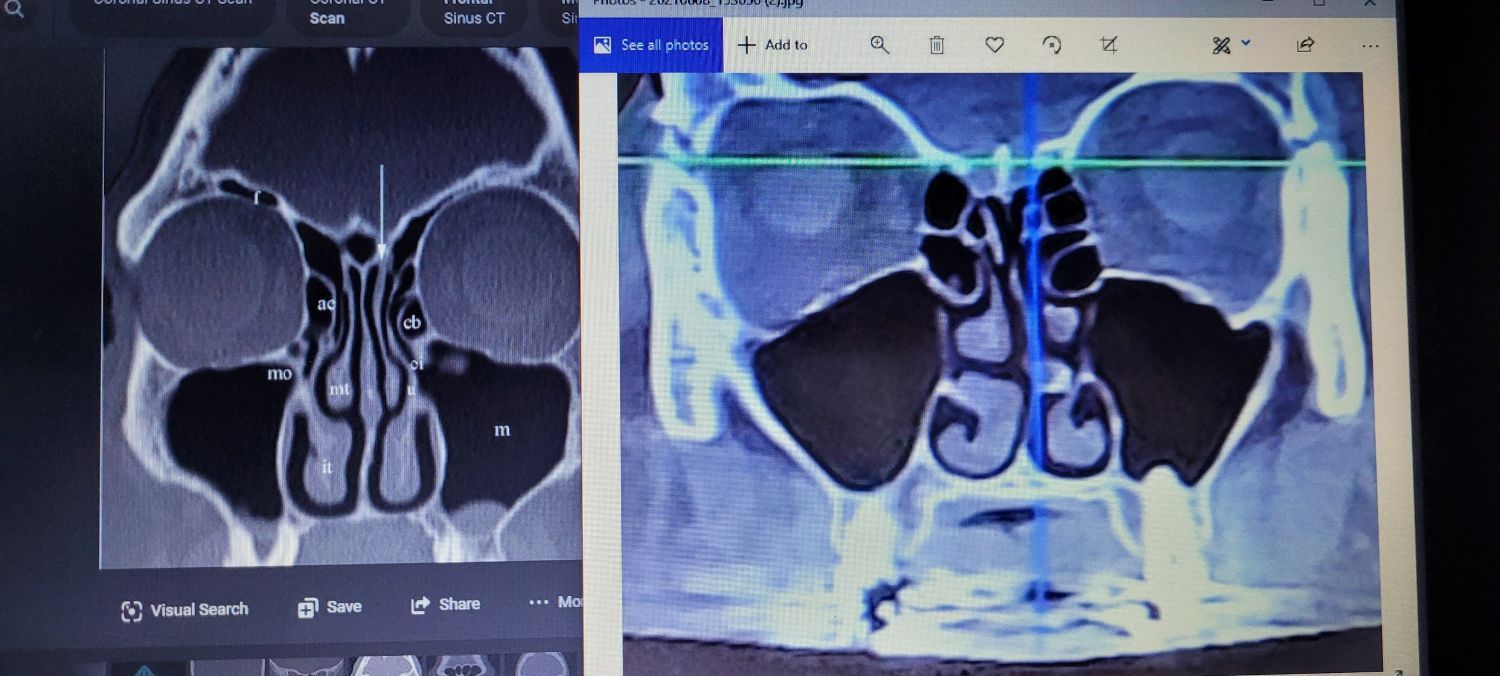
What Are the Differences Between Asthma and COPD?
Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are both common respiratory diseases and often have symptoms that overlap. It is easy to confuse the two conditions since both cause swelling in the airways, making breathing hard.
Although there are many similarities between asthma and COPD, there are also many differences. They are two distinct diseases with distinct causes, symptoms, types of airway inflammation, inflammatory cells, mediators, inflammation consequences, response to therapy, and course.
Around 40% of people with COPD also have asthma. Asthma is thought to be a risk factor for developing COPD. As you get older, your chances of getting this dual diagnosis increase.
Keep reading to understand the differences between asthma and COPD.
Causes
COPD is primarily caused by smoking-related damage, whereas an inflammatory response causes asthma.
Asthma is known to be triggered due to environmental triggers and possibly inherited genetic factors. Pollen, dust mites, mold, pet hair, respiratory infections, physical activity, cold air, smoke, some medications such as beta blockers and aspirin, stress, sulfites, preservatives added to some foods and beverages, and gastroesophageal reflux disease are all common asthma triggers.
The most common cause of COPD is long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke. Smoke irritates the lungs, causing the bronchial tubes and air sacs to lose their natural elasticity and over-expand, trapping air in the lungs when you exhale. A genetic disorder is yet another cause of COPD. This disorder leads to low levels of a protein called alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT), which protects the lungs.
Symptoms
The initial symptoms of both conditions seem similar, including shortness of breath, chest tightness, wheezing, and coughing, leading to confusion or misdiagnosis. Airway hyper-responsiveness is yet another common symptom in both disorders. However, asthma typically causes attacks of wheezing and chest tightness. COPD symptoms generally are more persistent and can include a cough that produces phlegm.
Asthma symptoms can come and go, and patients can be symptom-free for a long time. COPD symptoms are constant and can worsen over time, even with treatment.
Age
The primary distinction between COPD and asthma is often the patient's age. Asthma is typically diagnosed in children and teens, whereas COPD symptoms appear most often in adults over the age of 40.
Treatment and Care
Asthma is a long-term medical condition that can be managed by recognizing and avoiding the triggers. A few common asthma treatments include bronchodilators to open the airways, allergy medications, and long-term asthma medications, which help patients breathe easier.
The treatment methods for COPD differ from asthma, even though this is also a long-term condition that constricts airways. COPD worsens with time, and the main objective of the treatment would be to manage the symptoms and prevent the condition from getting worse.
Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke significantly helps in preventing COPD from getting worse. Nicotine replacement products, medications, therapy, hypnosis, and support groups are a few ways that can help quit smoking. Other treatments include inhalers, oral steroids, lung therapies, and sometimes lung surgeries (involving removing damaged lung tissues).
Asthma and COPD are both long-term conditions that can be well managed by proper medications and treatments. Know more about asthma, COPD, or any other condition affecting the airways from Snot Force Alliance, Inc. We bring together doctors and medical professionals to collaborate, innovate, and inspire the best of the medical community involved in treating nose, sinus, and airway conditions. Join the talented group today to learn and share!